본 글은 Udemy의 자바 자료구조 강의를 듣고 개인적으로 학습한 내용 복습하기 위해 작성된 글로 내용상 오류가 있을 수 있습니다. 오류가 있다면 지적 부탁 드리겠습니다.
1. Stack이란?
Stack은 한 쪽 끝에서만 항목을 삭제하거나 새로운 항목을 저장하는 자료구조이다.
스택에서 새로운 항목을 저장하는 연산을 push라고 하고, 항목을 삭제하는 연산을
pop이라고 한다.
- LIFO(Last In First Out) : 선입선출
- 대부분의 고수준의 언어(high level language)에서 스택은 Array나 Linked List로 쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
2. Stack 연산과정
2.1 Stack의 Push 연산
주어진 항목을 스택의 맨 위에 놓는 연산으로 O(1)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
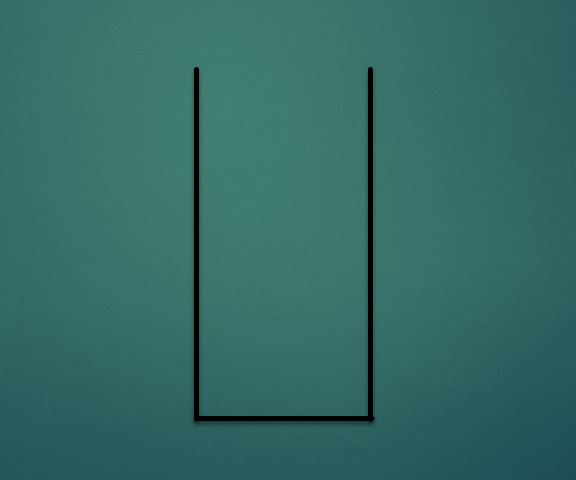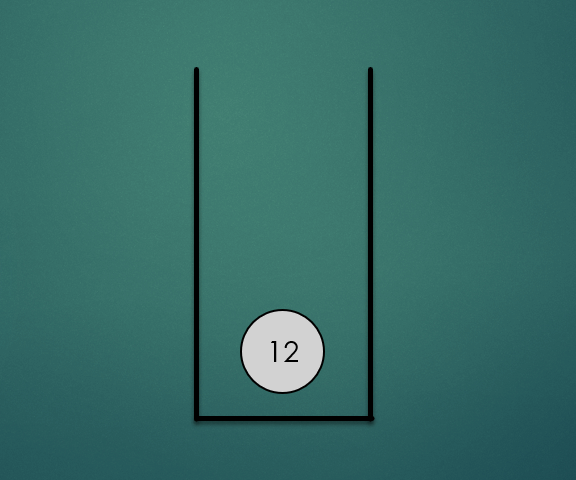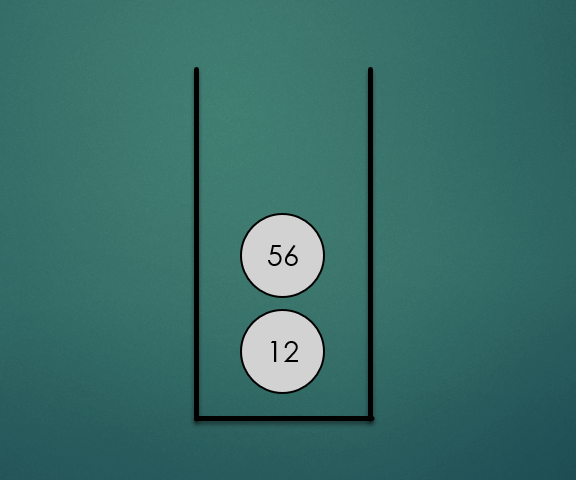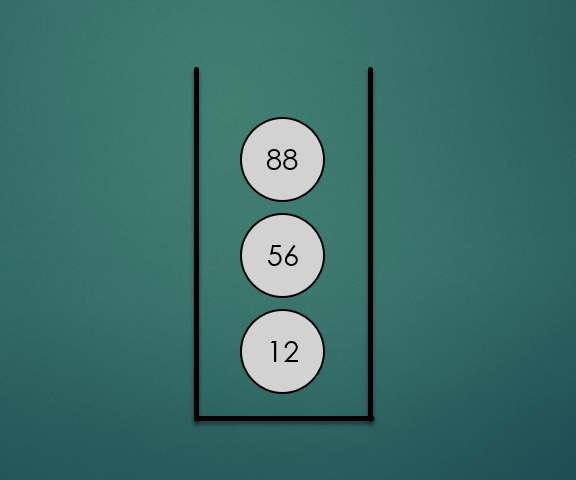
stack.push(12);
stack.push(56);
stack.push(88);
2.2 Stack의 Pop 연산
마지막으로 스택에 삽입한 항목을 제거하는 연산으로 O(1)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
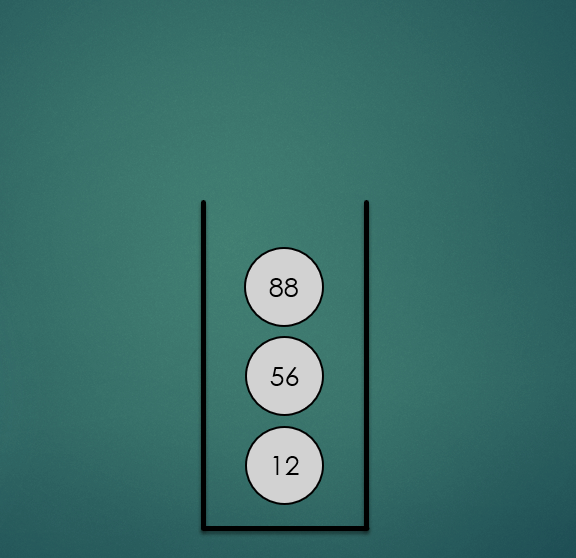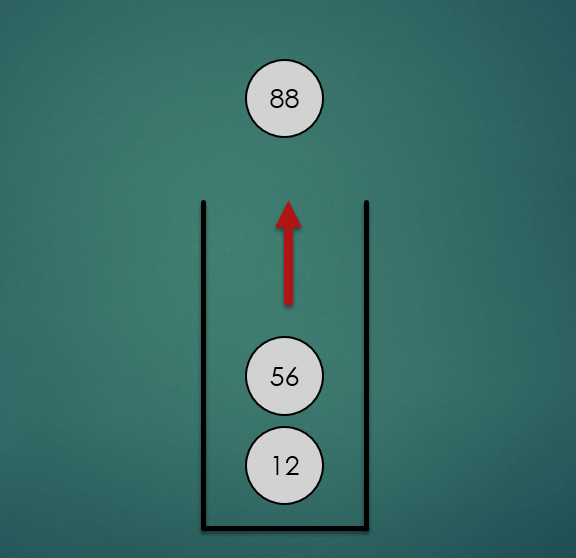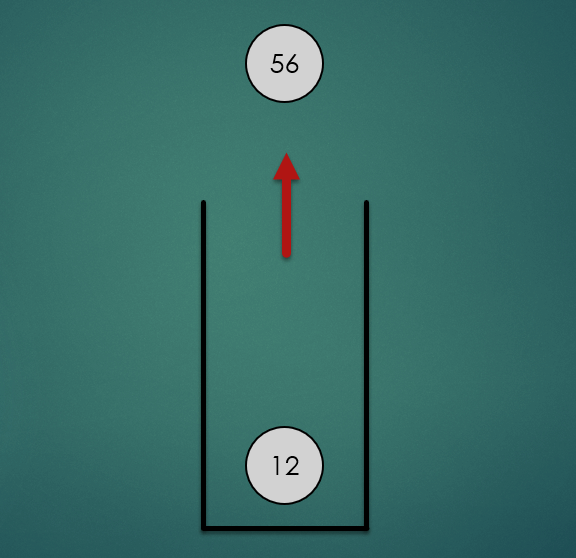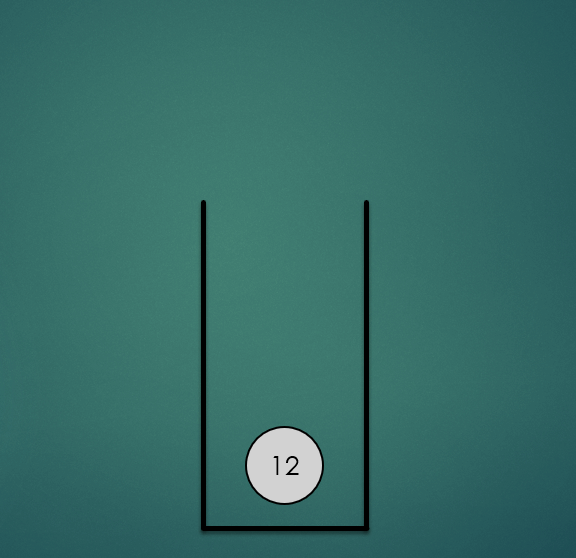
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
2.3 Stack의 Peek 연산
Stack의 맨 위의 항목을 제거하지 않고 반환하는 연산으로 O(1) 시간복잡도를 가진다.
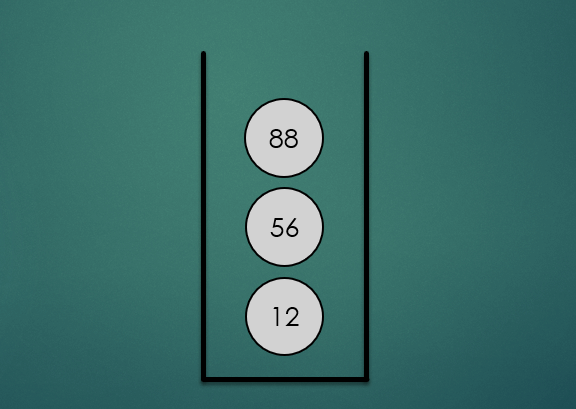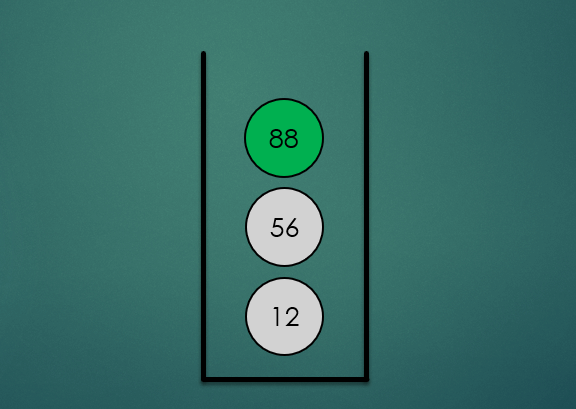
stack.peek();
3. Stack 메모리관리
3.1 Call Stack
- 프로그램의 코드 정보(서브루틴/메서드/함수)를 저장하는 Stack 자료구조이다.
- 세부 정보는 일반적으로 고급 프로그래밍 언어에서는 숨겨져있고, 자동화 되어있다.
- Stack은 현재 실행 중인 서브루틴을 실행한 다음 어디로 반환해야할지를 추적한다.
- 각 함수에 의해 생성된 임시 변수를 저장하는데도 쓰인다.
- 함수가 새로운 변수를 선언할 때 마다 Stack에 push가 된다.
- 함수를 종료할 때마다 모든 변수는 Stack에서 pop되고 영구적으로 사라지게 된다.
- local 변수는 Stack에 있다가 함수가 종료되면 사라지게 된다.
- Stack의 메모리는 제한적이다.
3.2 Heap meomory
- Heap은 자동으로 관리되지 않는 메모리 영역이다.
- Stack 메모리와 달리 대용량 메모리 영역이다.
- Java의 경우 레퍼런스 타입이나 객체(인스턴스)가 생성되는 공간이다.
- 메모리가 자동으로 관리되지 않기 때문에 할당을 해제해야만 한다.
- 그렇지 않으면 메모리 누수가 발생하여 느려질 수 있다.
3.3 Stack, Heap 비교
| stack memory | heap memory |
|---|---|
| 사이즈 제한 O | 사이즈 제한 X |
| 접근이 빠름 | 접근이 느림 |
| 지역변수 | 객체, 인스턴스 |
| CPU에 의해 공간이 효츌적으로 관리됨 | 메모리가 조각날수 있음 |
| 변수는 리사이즈 X | 변수는 리사이즈 O |
4. Stack 직접 구현해보기
4.1 Linked List로 구현
4.1.1 구현 코드
public class Node<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private T data;
private Node<T> nextNode;
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node<T> getNextNode() {
return nextNode;
}
public void setNextNode(Node<T> nextNode) {
this.nextNode = nextNode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data.toString();
}
}
public class Stack<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private Node<T> root;
private int count;
// O(1) 시간 복잡도
public void push(T newData) {
this.count++;
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = new Node<>(newData);
} else {
Node<T> oldRoot = this.root;
this.root = new Node<>(newData);
this.root.setNextNode(oldRoot);
}
}
// O(1) 시간 복잡도
public T pop() {
T itemToPop = this.root.getData();
this.root = this.root.getNextNode();
this.count--;
return itemToPop;
}
// O(1) 시간 복잡도
public T peek() {
return this.root.getData();
}
// O(1) 시간 복잡도
public int size() {
return this.count;
}
// O(1) 시간 복잡도
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.root == null;
}
}
4.1.2 테스트
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> myStack = new Stack<>();
myStack.push("A");
myStack.push("B");
myStack.push("C");
myStack.push("D");
System.out.println(myStack.peek());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.peek());
}
}
4.1.3 결과
D
D
C
B
A
4.2 Array로 구현
4.2.1 구현코드
public class Stack<T> {
private T[] stack;
private int numOfItems;
public Stack() {
this.stack = (T[]) new Object[1];
}
public void push(T newData) {
if (numOfItems == this.stack.length) {
resize(2 * this.stack.length);
}
this.stack[numOfItems++] = newData;
}
public T pop() {
T itemToPop = this.stack[--numOfItems];
if (numOfItems > 0 && numOfItems == this.stack.length / 4) {
resize(this.stack.length / 2);
}
return itemToPop;
}
public T peek() {
return this.stack[numOfItems - 1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.numOfItems == 0;
}
public int size() {
return this.numOfItems;
}
// O(N) 시간 복잡도
private void resize(int capacity) {
T[] stackCopy = (T[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < numOfItems; i++) {
stackCopy[i] = this.stack[i];
}
this.stack = stackCopy;
}
}
4.2.2 테스트
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> myStack = new Stack<>();
myStack.push("A");
myStack.push("B");
myStack.push("C");
myStack.push("D");
System.out.println("stack size : " + myStack.size());
System.out.println("stack peek : " + myStack.peek());
System.out.println("stack pop : " + myStack.pop());
System.out.println("stack pop : " + myStack.pop());
System.out.println("stack pop : " + myStack.pop());
System.out.println("stack peek : " + myStack.peek());
}
}
4.2.3 결과
stack size : 4
stack peek : D
stack pop : D
stack pop : C
stack pop : B
stack peek : A
6. Dijkstra’s interpreter
6.1 Dijkstra’s interpreter란?
- 수학식을 파싱하기 위한 메서드
- Shunting-yard 알고리즘은 stack을 기반으로 하나의 stack은 숫자를 또다른 stack은 연산자를 저장한다.
- Shunting-yard 알고리즘은 연산자를 우선으로 파싱하는데 일반적으로 사용한다.
6.2 Dijkstra’s interpreter 구현
6.2.1 구현코드
public class Algorithm {
private Stack<String> operationStack;
private Stack<Double> valueStack;
public Algorithm() {
this.operationStack = new Stack<>();
this.valueStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void interpreterExpression(String expression) {
String[] expressionArray = expression.split(" ");
for (String e : expressionArray) {
if (e.equals("(")) {
} else if (e.equals("+")) {
this.operationStack.push(e);
} else if (e.equals("*")) {
this.operationStack.push(e);
} else if (e.equals(")")) {
String operation = this.operationStack.pop();
if (operation.equals("+")) {
this.valueStack.push(this.valueStack.pop() + this.valueStack.pop());
} else if (operation.equals("*")) {
this.valueStack.push(this.valueStack.pop() * this.valueStack.pop());
}
} else {
this.valueStack.push(Double.parseDouble(e));
}
}
}
public void result() {
System.out.println(this.valueStack.pop());
}
}
6.2.2 테스트
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Algorithm algorithm = new Algorithm();
algorithm.interpreterExpression("( ( 1 + 2 ) * ( 3 + 4 ) )");
algorithm.result();
}
}
6.2.3 결과
21.0
7. Stack 문제해결
7.1 Max in a stack problem : Stack 최대값 찾기
- The aim is to design an algorithm that can return the maximum item of a stack in O(1) running time complexity. We can use O(N) extra memory!
- Hint: we can use another stack to track the max item
public class MaxItemStack {
private Stack<Integer> mainStack; // 원본 Stack
private Stack<Integer> maxStack; // 최대값을 구하기 위한 Stack
public MaxItemStack() {
this.mainStack = new Stack<>();
this.maxStack = new Stack<>();
}
// 삽입 연산
public void push(int item) {
mainStack.push(item); // 원본 Stack에 삽입
// 첫번째 삽입일 경우 mainStack과 같이 maxStack에 삽입
if (mainStack.size() == 1) {
maxStack.push(item);
return;
}
// 새롭게 삽입할 항목이 maxStack의 최대값보다 크면
if (item > maxStack.peek()) {
maxStack.push(item);
// 크지 않다면 기존의 최대값을 삽입
} else {
maxStack.push(maxStack.peek());
}
}
// 삭제 연산 : maxStack, mainStack 둘다 항목 제거
public int pop() {
maxStack.pop();
return mainStack.pop();
}
// 최대값 반환
public int getMaxItem() {
return maxStack.peek();
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MaxItemStack maxItemStack = new MaxItemStack();
maxItemStack.push(1);
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.push(2);
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.push(3);
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.push(5);
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.push(4);
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.push(7);
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.push(9);
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
System.out.println("-------after pop()-------");
maxItemStack.pop();
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.pop();
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.pop();
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
maxItemStack.pop();
System.out.println(maxItemStack.getMaxItem());
}
}
1
2
3
5
5
7
9
-------after pop()-------
7
5
5
3
7.2 Queue Implementation with Stacks : Stack으로 Queue 구현하기
- The aim is to design a queue abstract data type with the help of stacks.
해결책
- Stack의 도움을 받아 큐를 구현하기 위해서는 2개의 Stack을 사용하면된다.
- 첫번째 Stack은
enqueue()연산을 수행한다. - 두번째 Stack은
dequeue()연산을 수행한다.
public class Queue {
private Stack<Integer> enqueueStack;
private Stack<Integer> dequeueStack;
public Queue() {
this.enqueueStack = new Stack<>();
this.dequeueStack = new Stack<>();
}
// 삽입 연산
public void enqueue(int item) {
this.enqueueStack.push(item);
}
public int dequeue() {
if (enqueueStack.isEmpty() && dequeueStack.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stacks are empty...");
}
if (dequeueStack.isEmpty()) {
while (!enqueueStack.isEmpty()) {
dequeueStack.push(enqueueStack.pop());
}
}
return dequeueStack.pop();
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(10);
queue.enqueue(5);
queue.enqueue(20);
queue.enqueue(1);
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
queue.enqueue(100);
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
}
}
10
5
20
1
7.3 Queue Implementation with Stacks : Stack으로 Queue 구현하기 2
해결책
- 재귀호출을 통해 Stack 하나로 Queue를 구현할 수 있다.
public class Queue {
// Stack 선언
private Stack<Integer> stack;
// 생성자
public Queue() {
this.stack = new Stack<>();
}
// Queue 삽입연산
public void enqueue(int item) {
this.stack.push(item);
}
// Queue 삭제 연산 : Stack 하나만을 사용하여 구현, call stack을 통한 재귀호출
public int dequeue() {
// Stack 사이즈가 1이면 삭제 연산 수행 : 마지막 항목이면 삭제처리
if (stack.size() == 1) {
return stack.pop();
}
// 미자막 항목을 찾을 때까지 pop 연산을 수행
int item = stack.pop();
// 재귀 호출 수행
int lastDequeueItem = dequeue();
// 꺼낸 항목을 다시 삽입
enqueue(item);
// 마지막 항목 반환
return lastDequeueItem;
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(10);
queue.enqueue(5);
queue.enqueue(20);
queue.enqueue(1);
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
queue.enqueue(100);
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
}
}
10
5
20
1