본 글은 Udemy의 자바 자료구조 강의를 듣고 개인적으로 학습한 내용 복습하기 위해 작성된 글로 내용상 오류가 있을 수 있습니다. 오류가 있다면 지적 부탁 드리겠습니다.
1. Hashtable이란?
1.1 Hashtable 기본개념
O(logN)보다 빠른 연산을 위해 키와 1차원 배열의 인덱스의 관계를 이용하여 키(항목)을 저장하는 자료구조를 해시테이블이라고 한다. 해시테이블은 키를 간단한 해시함수로 계산한 값을 배열의 인덱스로 이용하여 항목을 저장하고 탐색/삭제하는 연산을 평균 O(1) 시간복잡도로 지원하는 자료구조이다.
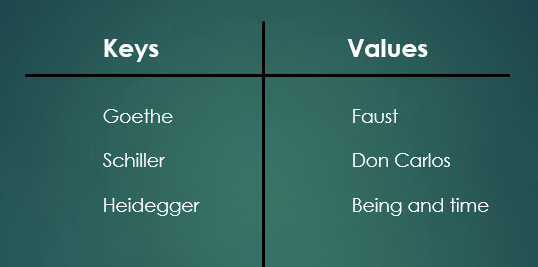
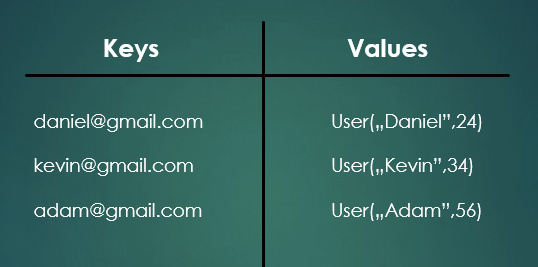
위의 그림과 같이 소설의 저자를 키로 제목을 값으로 또는 회원의 이메일을 키, 회원정보를 값으로 저장할 수도 있다. 이렇게 저장된 값을 탐색,수정,삭제 할 때에는 소설의 저자, 회원의 이메일을 통해 접근할 수 있다.

일반적으로 배열에 회원을 저장하거나 특정 회원을 탐색하는 상황을 생각해보자. 배열의 인덱스를 통한 삽입이나 탐색 연산은 O(1) 시간복잡도를 가지게 된다.
하지만 해시테이블의 경우 배열의 인덱스를 키값으로 가지고 있는 것이 아니라 위에서 봤듯이 회원의 이메일을 키값으로 가지고 있기 때문에 키값을 해시함수를 통해 배열의 인덱스로 변환하는 과정을 거치야 한다.
index = h(key) // h()는 해시함수를 의미하고, 배열의 인덱스에 키를 맵핑한다.
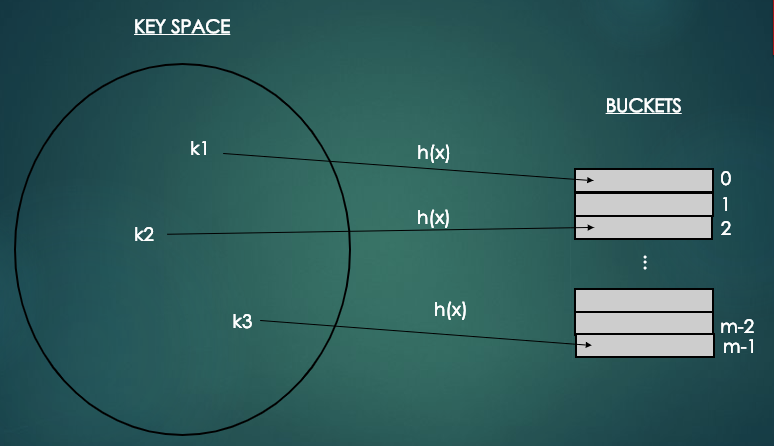
해시함수는 키들을 균등하게 해시테이블의 인덱스로 변환하기 위해 의미가 부여되어 있는 키를 간단한 계산을 통해 해시테이블 크기에 맞게 해시값을 계산한다.
n: 키의 숫자를 의미m: 배열의 버킷 수 또는 크기(사이즈)를 의미h(x) = n % m: 해시함수로 나머지 연산으로 대표적인 함수
해시함수가 균등한 결과를 보장하더라도 함수 계산 자체에 긴 시간이 소요되면 해싱의 장점인 연산의 신속성을 잃게된다. 따라서 단순하면서도 동시에 키들을 균등하게 변환하는 해시함수가 바람직하다.
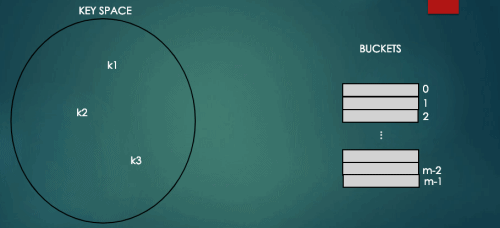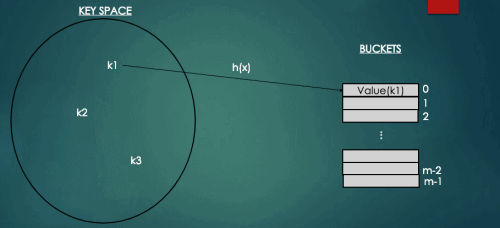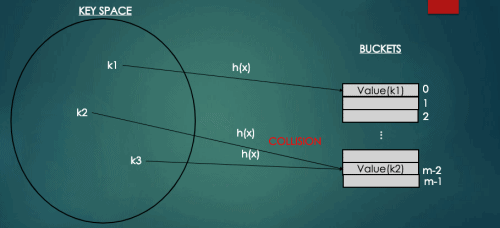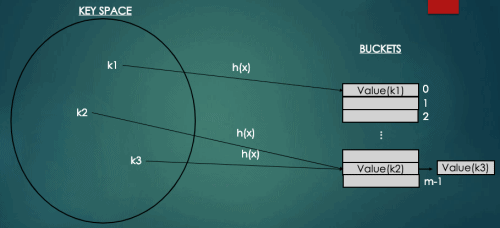
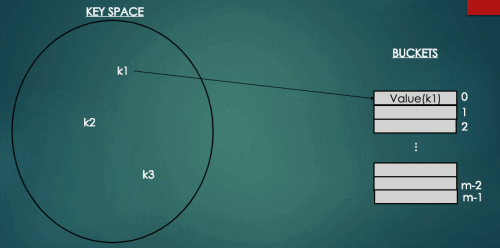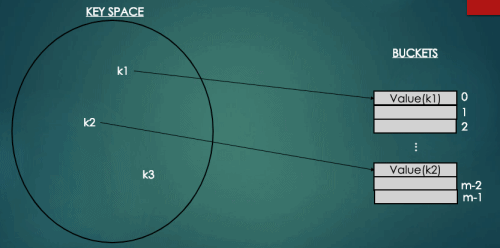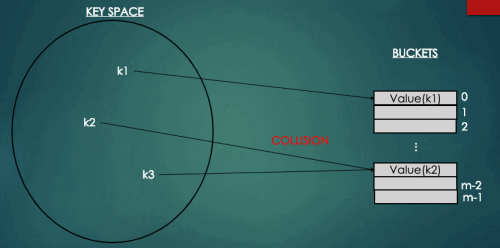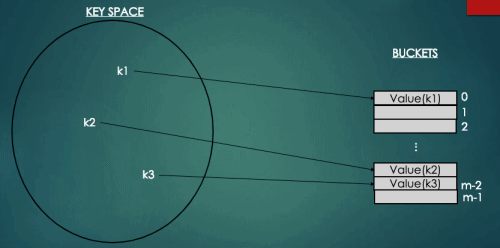
2. Collision(충돌)
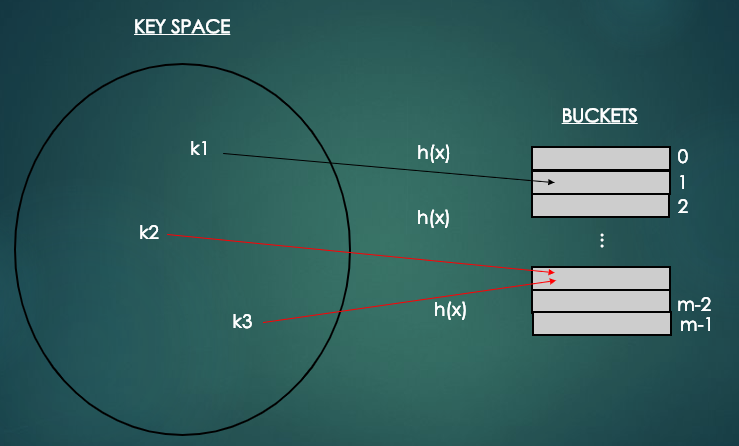
위의 그림과 같이 서로 다른 키값에 대해서 해싱함수에 의해 주어진 버킷이 같은 경우를 충돌(Collision)이라고 한다.
2.1 Closed Addressing(폐쇄주소방식) - Chaining
폐쇠주소방식은 키에 대한 해시값에 대응되는 곳에만 키를 저장한다. 따라서 충돌이 발생한 키들은 한 위치에 모여 저장되는데 이를 구현하는 대표적인 방법이 체이닝(Chaining)이다.
체이닝은 키를 해시값에 대응되는 연결리스트에 저장하는 해시방식으로 연결리스트로 구현되어 참조값을 차지하는 공간이 추가로 필요하다는 단점이 있다. 하지만 개방주소방식과 같이 empty원소를 찾는 오버헤드와 군집화가 없으며 구현이 간결하여 실제로 가장 많이 활용되는 방식이다.
2.2 Open Addressing(개방주소방식) - Linear Probing
개방주소방식은 해시테이블 전체를 열린 공간으로 가정하여 충돌된 키를 일정한 방식에 따라 찾아낸 emepty 원소에 저장한다. 대표적인 방법은 선형조사(Linear Probing)와 이차조사(Quadratic Probing), 랜덤조사(Random probing) 등이 있다.
선형조사는 충돌이 일어난 원소에서부터 순차적으로 검색하여 처음 발견한 empty 원소에 충돌이 일어난 키를 저장한다. 즉 h(x) = i라면 해시테이블에 a[i], a[i+1], a[i+2], … ,a[i+j]를 차례로 검색하여 첫 번째로 찾아낸 empty 원소에 키를 저장하는 방식이다.
선형조사는 순차탐색으로 empty 원소를 찾아 충돌된 키를 저장하므로 해시테이블의 키들이 빈틈없이 뭉쳐지는 현상이 발생한다. 이를 군칩화(Primary Clustering)이라고 하는데 탐색, 삽입, 삭제 연산시 군집된 키들을 순차적으로 방문해야하는 문제점을 일으킨다. 이러한 군집화는 해시테이블에 empty원소 수가 적을수록 더 심화되며 해시성능을 저하시킨다.
3. 동적해싱(Dynamic resizing)
해시테이블에 비어있는 원소가 적으면, 삽입에 실패하거나 해시성능이 급격히 적어지는 현상이 발생한다. 성능은 적재율(Load Factor)에 따라 달라진다.
- 적재율이란
N(테이블에 저장된 키의 수) / N(테이블의 크기)이다. - 적재율은 1과 가까워질수록 해시테이블은 거의 다 차있어 성능이 낮아지게 되고, 연산이 느려지게 된다.
- 적재율이 0과 가까워질수록 해시테이블은 거의 비어있어 메모리를 낭비하게 된다.
- 적재율을
a라고 한다면 일반적으로a >= 0.75가 되면 해시테이블의 크기를 2배로,a <= 0.25가 되면 해시테이블을 1/2로 줄인다.
4. Hashtable 구현
4.1 Chaining
4.1.1 클래스 작성
// HashItem 클래스 : 키와 값을 저장할 클래스
public class HashItem {
private int key; // 키
private int value; // 값
private HashItem nextHashItem; // 다음 항목
// 생성자
public HashItem(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
// getter, setter 생략...
}
// Constants 클래스 : 해시테이블의 크기를 상수로 보관
public class Constants {
private Constants() {
}
public static final int TABLE_SIZE = 10;
}
// HashTable 클래스
public class HashTable {
private HashItem[] hashTable;
// 생성자
public HashTable() {
this.hashTable = new HashItem[Constants.TABLE_SIZE];
}
// 해시 함수
private int hash(int key) {
// 키 % 테이블 사이즈 : 나머지 연산
return key % Constants.TABLE_SIZE;
}
// put() 메서드 작성
// get() 메서드 작성
}
4.1.2 put() 메서드
// 삽입
public void put(int key, int value) {
// 키를 해싱
int hashArrayIndex = hash(key);
// 해시 테이블의 슬롯이 비어 있으면 바로 삽입
if (hashTable[hashArrayIndex] == null) {
System.out.println("no collision simple insertion");
hashTable[hashArrayIndex] = new HashItem(key, value);
} else { // 해쉬 테이블의 슬롯이 비어있지 않으면
System.out.println("collision when inserting with key : " + key);
HashItem hashItem = hashTable[hashArrayIndex]; // 해쉬테이블 슬롯에 저장된 첫번째 데이터를 가져온다.
// 연결리스트 마지막까지 탐색를 수행
while (hashItem.getNextHashItem() != null) {
hashItem = hashItem.getNextHashItem();
System.out.println("Considering the next item in linked list " + hashItem.getValue());
}
// 마지막으로 연결 리스트 다음에 삽입
System.out.println("Finally we have found the place to insert...");
hashItem.setNextHashItem(new HashItem(key, value));
}
}
4.1.3 get() 메서드
// 반환
public int get(int key) {
// 입력받은 키값을 해싱
int generatedArrayIndex = hash(key);
// 해시 값에 해당하는 슬롯에 데이터가 없으면 -1 리턴
if (hashTable[generatedArrayIndex] == null) {
return -1;
} else { // 해시 값에 해당하는 슬롯에 데이터가 있는 경우
// 첫번째 항목 추출
HashItem hashItem = hashTable[generatedArrayIndex];
// 입력 키 값과 항목의 키 값이 일치할 때까지 탐색
while (hashItem != null && hashItem.getKey() != key) {
hashItem = hashItem.getNextHashItem();
}
// 마지막까지 탐색한 뒤 일치하는 값을 못찾은 경우 -1 리턴
if (hashItem == null) {
return -1;
} else { // 값 리턴
return hashItem.getValue();
}
}
}
4.1.4 테스트 결과
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTable hashTable = new HashTable();
hashTable.put(1, 10);
hashTable.put(2, 20);
hashTable.put(3, 30);
hashTable.put(4, 40);
hashTable.put(5, 50);
hashTable.put(6, 60);
hashTable.put(7, 70);
hashTable.put(8, 80);
hashTable.put(9, 90);
hashTable.put(10, 100);
hashTable.put(11, 110); // 출동 발생
hashTable.put(12, 120); // 충돌 발생
hashTable.put(22, 220); // 충돌 발생
System.out.println(hashTable.get(11));
System.out.println(hashTable.get(12));
System.out.println(hashTable.get(2));
System.out.println(hashTable.get(222)); // 찾는 항목이 존재하지 않기 때문에 -1 리턴
}
}
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
no collision simple insertion
collision when inserting with key : 11
Finally we have found the place to insert...
collision when inserting with key : 12
Finally we have found the place to insert...
collision when inserting with key : 22
Considering the next item in linked list 120
Finally we have found the place to insert...
110
120
20
-1
4.2 Linear Probing
4.2.1 클래스 작성
public class HashItem {
private int key; // 키
private int value; // 값
public HashItem(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
// getter, setter ...
}
public class Constants {
public Constants() {
}
public static final int TABLE_SIZE = 10;
}
public class HashTable {
private HashItem[] hashTable;
// 생성자
public HashTable() {
this.hashTable = new HashItem[Constants.TABLE_SIZE];
}
// 해시 함수
private int hash(int key) {
//return key % Constants.TABLE_SIZE;
return 0; // 테스트에서 충돌이 바로 일어나도록 변경
}
// put() 메서드
// get() 메서드
}
4.2.2 put 메서드
// 삽입
public void put(int key, int value) {
int generatedIndex = hash(key); // 키 해싱
System.out.println("put() method called with value : " + value + ", generatedIndex : " + generatedIndex);
// 충돌이 없을 때까지 반복 수행
while (hashTable[generatedIndex] != null) {
// 인덱스 1씩 증가
generatedIndex = (generatedIndex + 1) % Constants.TABLE_SIZE;
System.out.println("Collision -> move to next index : " + generatedIndex);
}
// 빈 슬롯에 항목 삽입
System.out.println("Inserted finally with index : " + generatedIndex);
hashTable[generatedIndex] = new HashItem(key, value);
}
4.2.3 get 메서드
// 반환
public int get(int key) {
int generatedIndex = hash(key); // 키 해싱
// 입력받은 키값이 동일할 때까지 반복 수행
while (hashTable[generatedIndex] != null && hashTable[generatedIndex].getKey() != key) {
// 인덱스 1씩 증가
generatedIndex = (generatedIndex + 1) % Constants.TABLE_SIZE;
System.out.println("Not Matched : move to next index : " + generatedIndex);
}
// 키에 대응하는 값을 찾지 못한 경우 -1을 리턴
if (hashTable[generatedIndex] == null) {
return -1;
} else { // 키에 대응하는 값을 반환
return hashTable[generatedIndex].getValue();
}
}
4.2.4 테스트
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTable hashTable = new HashTable();
hashTable.put(1, 10);
System.out.println();
hashTable.put(2, 20);
System.out.println();
hashTable.put(3, 30);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(hashTable.get(3));
}
}
put() method called with value : 10, generatedIndex : 0
Inserted finally with index : 0
put() method called with value : 20, generatedIndex : 0
Collision -> move to next index : 1
Inserted finally with index : 1
put() method called with value : 30, generatedIndex : 0
Collision -> move to next index : 1
Collision -> move to next index : 2
Inserted finally with index : 2
Not Matched : move to next index : 1
Not Matched : move to next index : 2
30
4.3 Generic Linear Probing
4.3.1 클래스 작성
// 해시테이블
public class HashTable<Key, Value> {
private Key[] keys; // 키 테이블
private Value[] values; // 값 테이블
private int numOfItems; // 해시테이블에 저장된 항목의 수
private int capacity; // 해시테이블의 사이즈
// 기본 생성자
public HashTable() {
this.keys = (Key[]) new Object[Constants.TABLE_SIZE];
this.values = (Value[]) new Object[Constants.TABLE_SIZE];
this.numOfItems = 0;
this.capacity = Constants.TABLE_SIZE;
}
// 사이즈 반환
public int size() {
return this.numOfItems;
}
// 해시테이블이 비었는지 확인
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.numOfItems == 0;
}
// 해시 함수
public int hash(Key key) {
//return key.hashCode() % this.capacity;
// 음수값을 반환하지 않도록 abs() 메서드 사용
return Math.abs(key.hashCode()) % this.capacity;
}
// put() 메서드
// get() 메서드
// remove() 메서드
// resize() 메서드
}
// 해시테이블의 사이즈
public class Constants {
public Constants() {
}
public static final int TABLE_SIZE = 10;
}
4.3.2 put() 메서드
// 삽입
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
// 삽입 값이 없으면 메서드 종료
if (key == null || value == null) {
return;
}
// 해시테이블 슬롯이 거의다 차있으면 슬롯 수를 2배 증가 : 동적 해싱
if (numOfItems >= capacity * 0.75) {
resize(2 * capacity);
}
// 키 해싱
int index = hash(key);
// 해시테이블 슬롯의 빈공간을 찾을 때까지 반복 수행
while (keys[index] != null) {
// 이미 키값과 동일한 데이터가 존재하면 업데이트 수행
if (keys[index].equals(key)) {
values[index] = value;
return;
}
// 반복 수행을 위해 인덱스 1 증가
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
}
// 슬롯의 빈공간에 삽입처리
keys[index] = key;
values[index] = value;
numOfItems++;
}
4.3.3 get() 메서드
// 탐색
public Value get(Key key) {
// 키 값이 null 이면 메서드 종료
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
int index = hash(key); // 키 값 해싱
// 해시 키값에 대응하는 해시 키값을 찾을 때까지 탐색
while (keys[index] != null) {
// 입력한 키값에 대응하는 키값이 해시테이블에 존재하면 값을 반환
if (keys[index].equals(key)) {
return values[index];
}
// 반복 수행을 위해 인덱스 1 증가
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
}
return null;
}
4.3.4 remove() 메서드
// 삭제
public void remove(Key key) {
// 키 값이 null 이면 메서드 종료
if (key == null) {
return;
}
int index = hash(key); // 키 값을 해싱
// 해시테이블에 입력한 키 값에 대응하는 키 값이 존재하지 않을 때까지 탐색
while (!keys[index].equals(key)) {
// 반복 수행 인덱스 1씩 증가
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
}
// 해당 키와 값 제거
keys[index] = null;
values[index] = null;
// 삭제 뒤 해시테이블을 재구성을 하지 않으면 공백이 생기고
// get() 메서드가 제대로 작동하지 않게 된다.
// 해시테이블 재구성을 위해 인덱스 1 증가
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
// 삭제한 슬롯 다음의 슬롯을 한칸 씩 앞으로 이동
while (keys[index] != null) {
Key tempKey = keys[index]; // 이동할 키 할당
Value tempValue = values[index]; // 이동할 값 할당
keys[index] = null; // 키 제거
values[index] = null; // 값 제거
numOfItems--; // put()메서드에서 다시 증가시키기 때문에 배열 사이즈 1 감소
put(tempKey, tempValue); // 앞의 슬롯에 삽입
// 인덱스 1 증가
index = (index + 1) % capacity;
}
numOfItems--; // 삭제 처리 후 배열 사이즈 1 감소
// 배열의 항목 수가 테이블의 크기보다 1/3보다 작으면 1/2로 사이즈 감소
if (numOfItems <= capacity / 3) {
resize(capacity / 2);
}
}
4.3.5 resize() 메서드
// 사이즈 변환
public void resize(int newCapacity) {
System.out.println("Resize table with new capacity : " + newCapacity);
HashTable<Key, Value> newTable = new HashTable<>(newCapacity); // 새로운 해시테이블 생성
// 기존의 해시테이블의 키와 값을 크가기 변경된 해시테이블에 저장
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
if (keys[i] != null) {
newTable.put(keys[i], values[i]);
}
}
keys = newTable.getKeys(); // 새로운 해시테이블의 키 할당
values = newTable.getValues(); // 새로운 해시테이블의 값 할당
capacity = newTable.getCapacity(); // 새로운 해시테이블의 사이즈 할당
}
private Key[] getKeys() {
return keys;
}
private Value[] getValues() {
return values;
}
private int getCapacity() {
return capacity;
}
4.3.6 테스트
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTable<String, Integer> hashTable = new HashTable<>();
hashTable.put("Doubles", 85);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Kim", 90);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Lee", 80);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Park", 100);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Choi", 88);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Son", 70);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Yoon", 82);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Mike", 88);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("James", 98);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Silvia", 100);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Olivia", 70);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Sophia", 85);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
hashTable.put("Harry", 70);
System.out.println(hashTable.size());
System.out.println(hashTable.get("park")); // null 반환
System.out.println(hashTable.get("Park"));
hashTable.remove("Harry");
hashTable.remove("Yoon");
hashTable.remove("Mike");
hashTable.remove("Kim");
hashTable.remove("Park");
hashTable.remove("Son");
hashTable.remove("Lee");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Resize table with new capacity : 20
9
10
11
12
13
null
100
Resize table with new capacity : 10