1. HashMap 장단점
1.1 장점
- HashMap은 매우 효율적인 자료구조로 중요한 연산(삽입, 탐색)들에 O(1) 시간복잡도를 가진다.
1.2 단점
- HashMap은 정렬을 지원하지 않는다.
- Hash함수는 왼벽하지 않기 때문에 충돌이 발생하게 된다.
위의 단점을 보완할 수 있는 자료구조는 Trie로 HashMap에서 발생하는 충돌을 제거하고, 정렬을 지원한다.
2. Trie 기본 개념
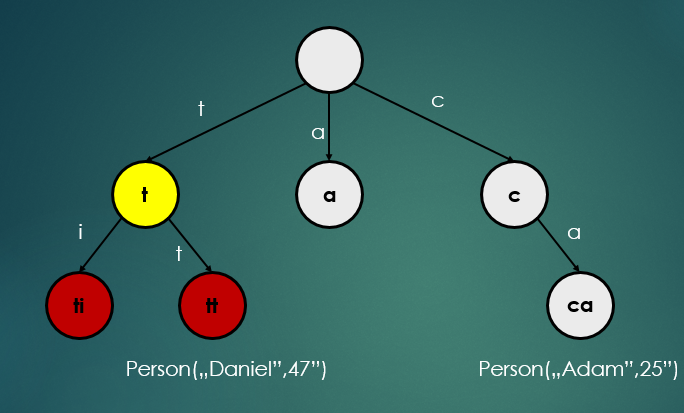
- Tire / Radix Tree / Prefix Tree 라고 부른다.
- 배열을 통해 자료구조를 구현할 수 있다.
- key는 일반적으로 문자열(String)이다.
- 노드의 모든 하위 항목에는 해당 노드와 연결된 문자열의 공통 접두사가 있으며 루트 노드는 빈 문자열을 저장한다.
- 값이 모든 노드에 저장되지 않고, 보통 마지막 노드(leaf node)에만 존재한다.
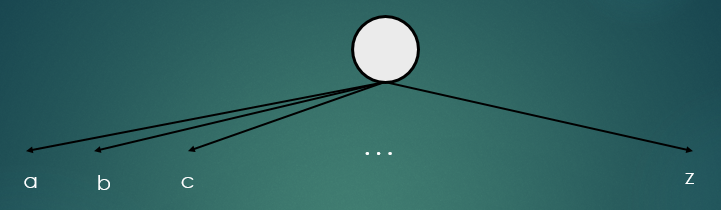
- 노드는 일반적으로 알파벳 수 만큼 하위노드를 가지고 있다.
- 모든 노드에서 사용이 가능하도록 알파벳 사이즈 만큼의 상수를 미리 선언하는 것이 좋다.
class Node {
value;
children[ALPHABET_SIZE] Node;
}
- 모든 노드들이 알파벳 수 만큼 하위노드를 가질 필요가 없을 경우가 존재하기 때문에 메모리 측면에서는 비효율적이다.
3. Trie 연산
3.1 삽입
Trie의 삽입 연산은 아래와 같이 이루어진다.
3.1.1 “apple” 삽입
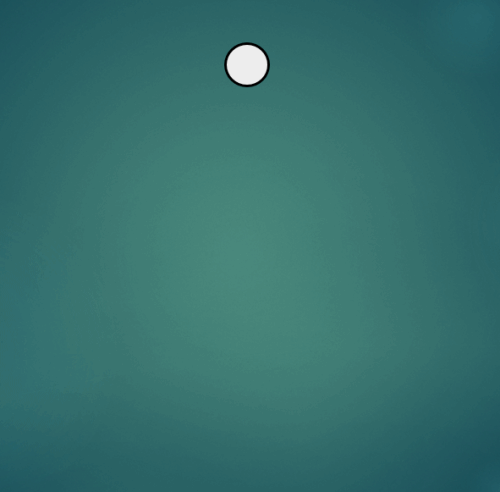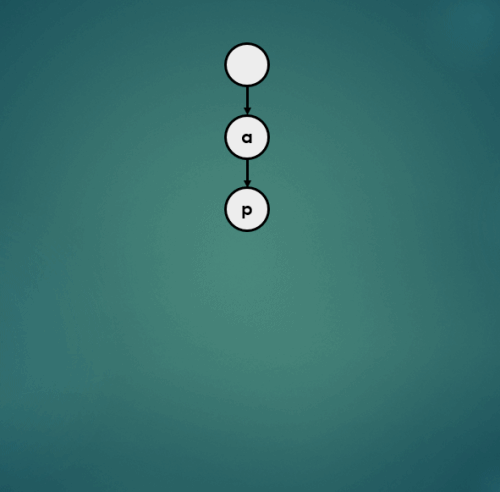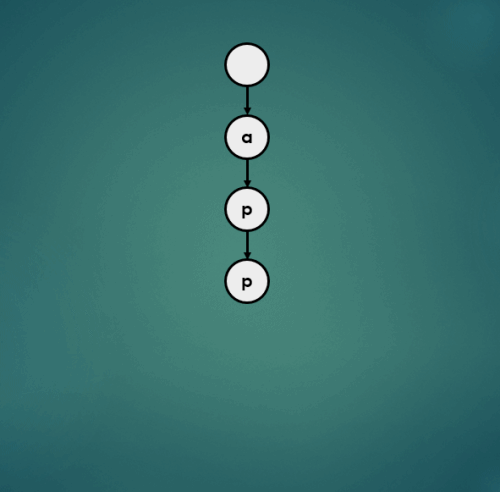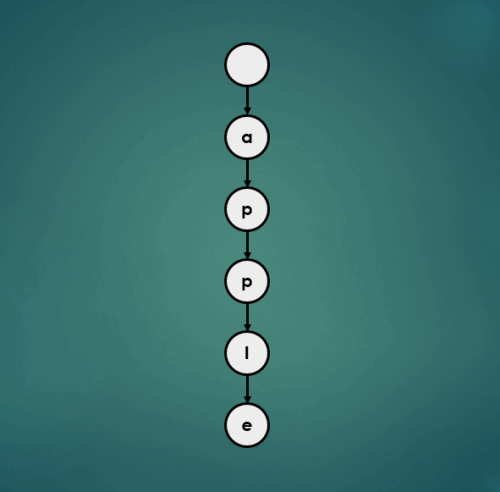
3.1.2 “air” 삽입
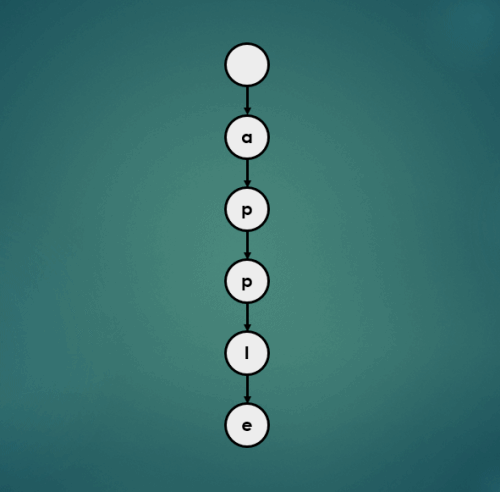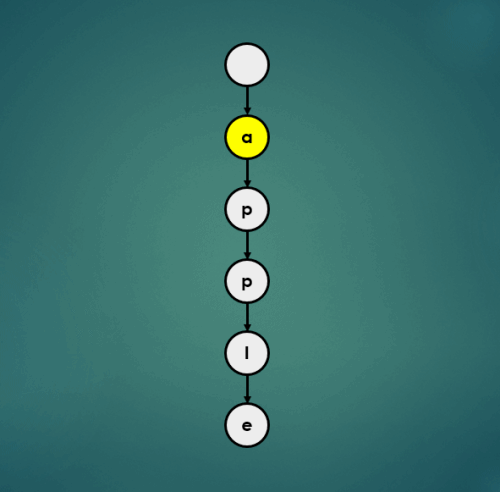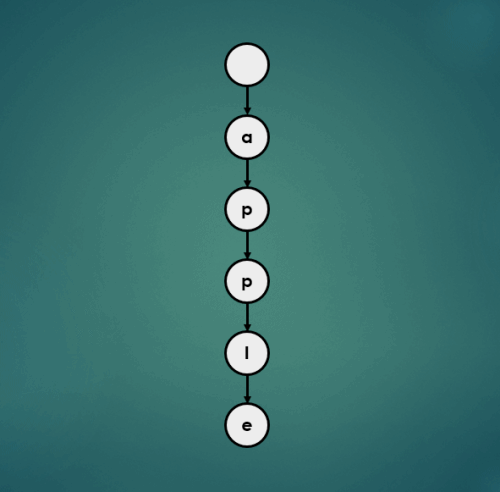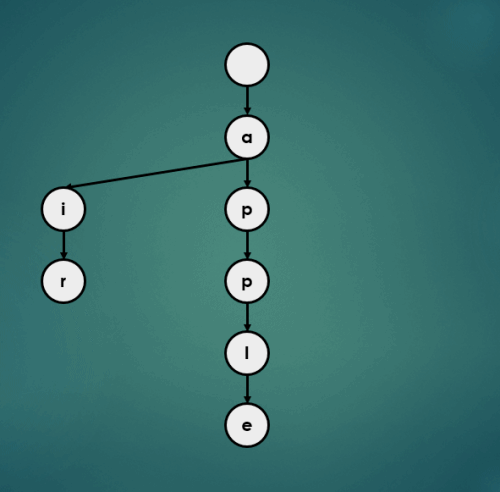
3.1.3 “approve” 삽입
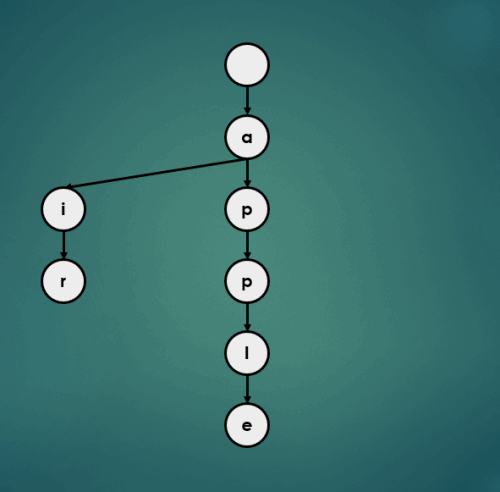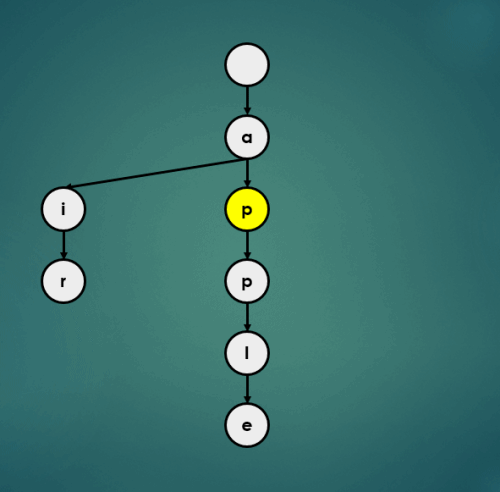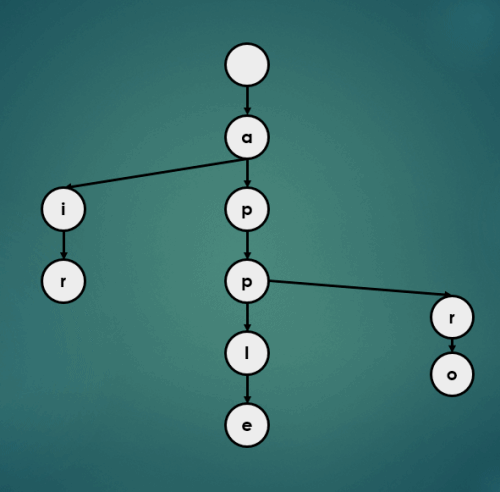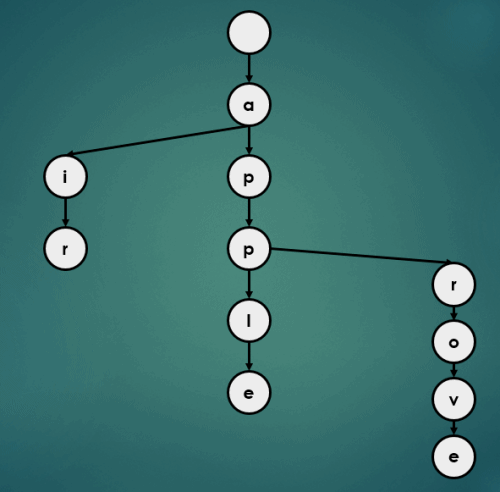
3.1.4 “appa” 삽입
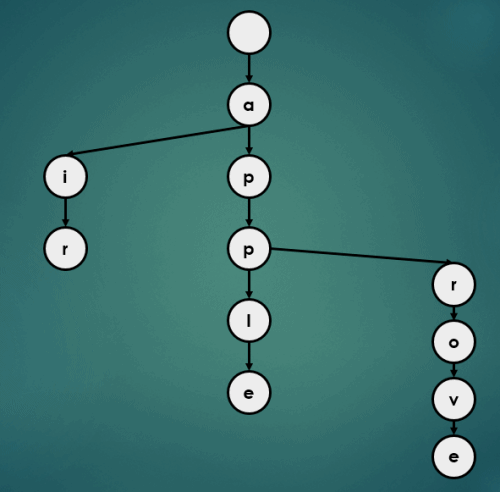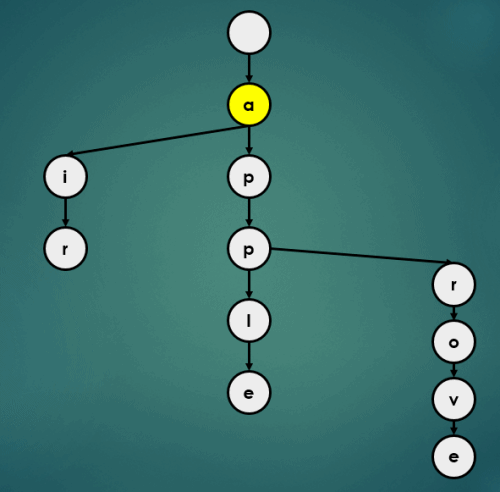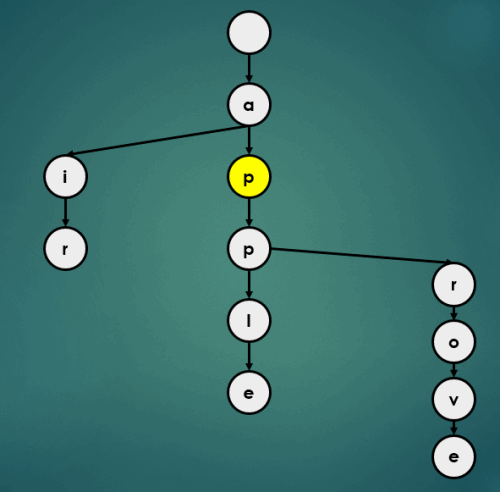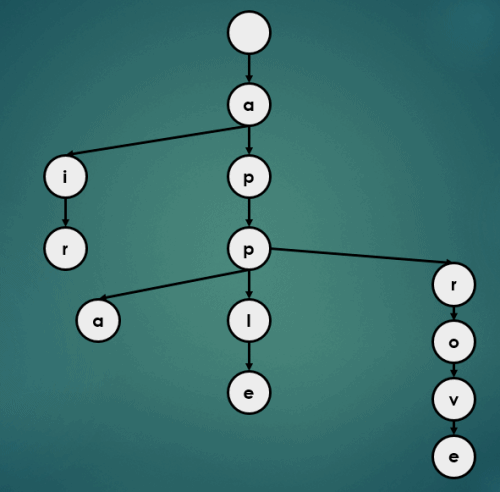
3.1.5 “appb” 삽입
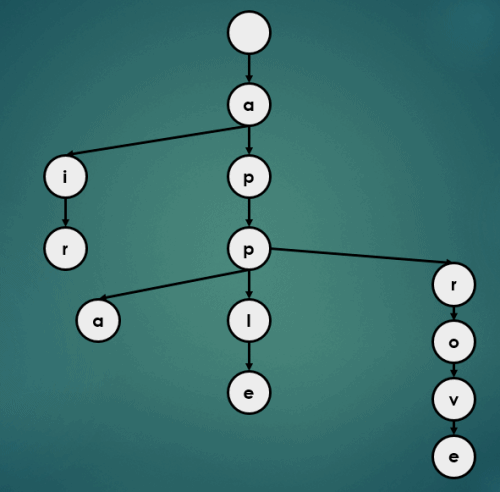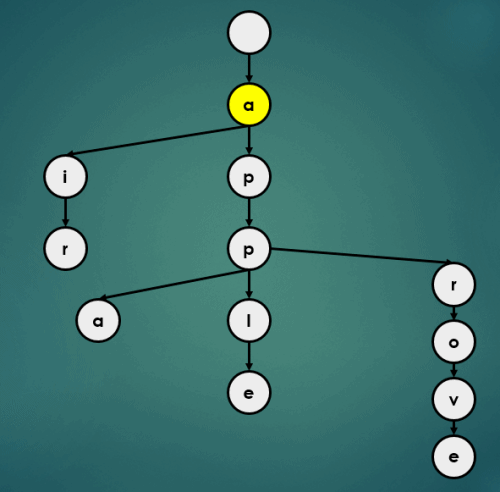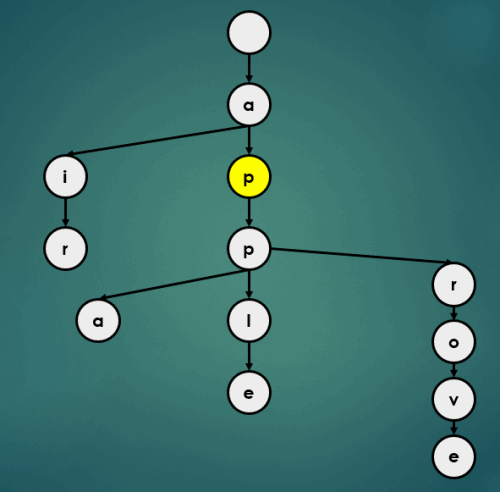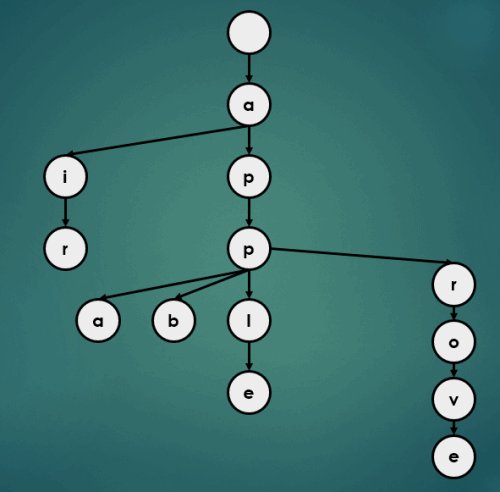
3.2 정렬
Trie의 정렬 연산은 아래와 같이 이루어진다.
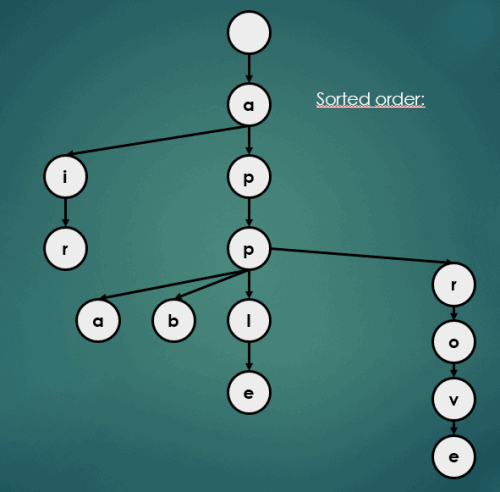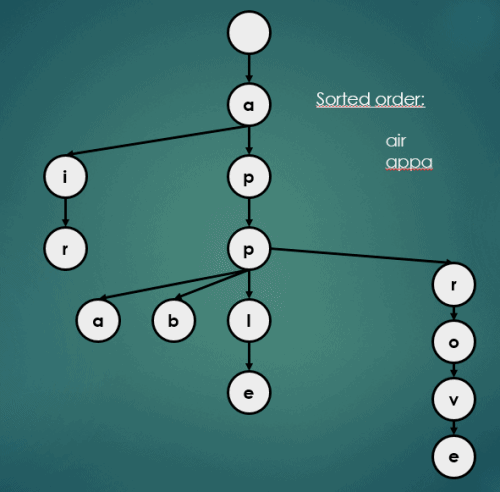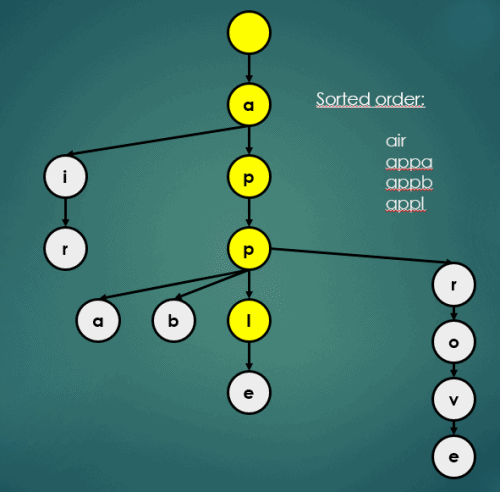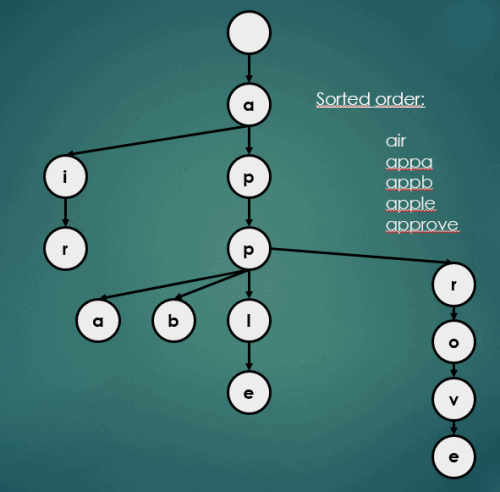
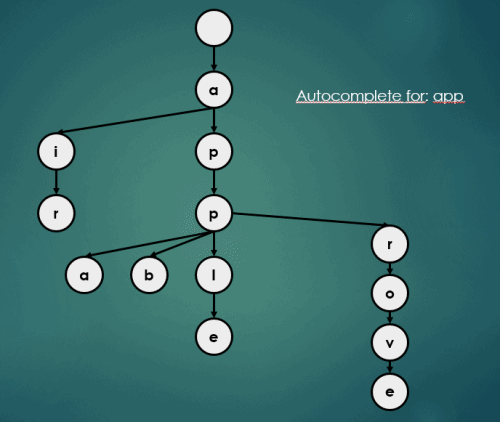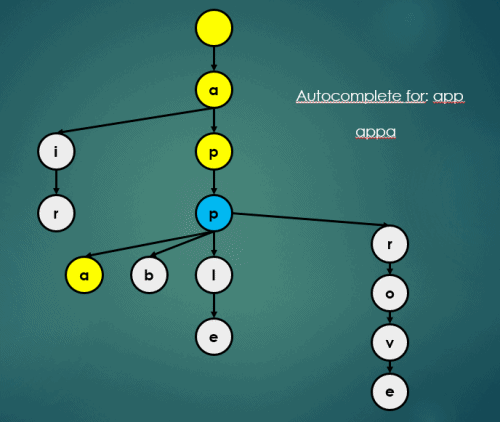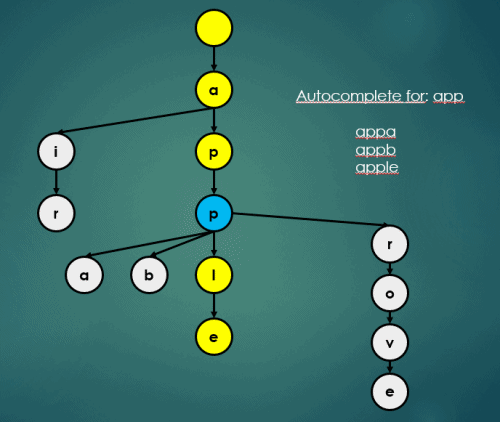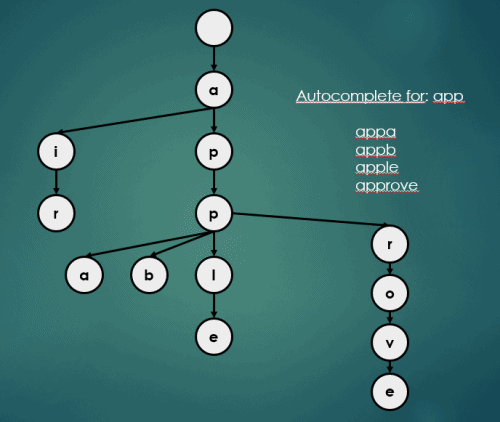
3.3 자동완성
Trie의 자동완성 연산은 아래와 같이 이루어진다.
3.4 Map처럼 삽입
Trie에서 Map처럼 데이터를 저장하는 과정은 아래와 같다.
3.4.1 “apple”을 키로 가진 데이터 1 삽입

put("apple", 1);
3.4.2 “air”을 키로 가진 데이터 2 삽입
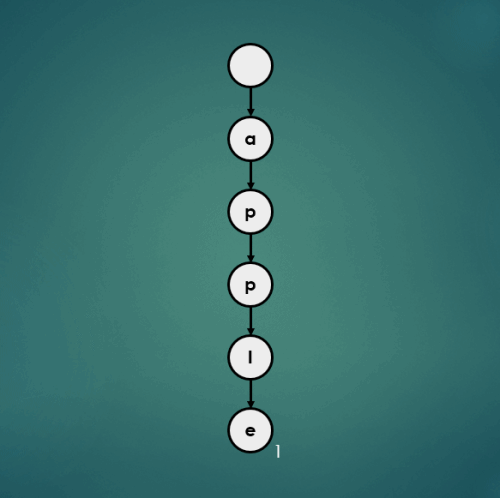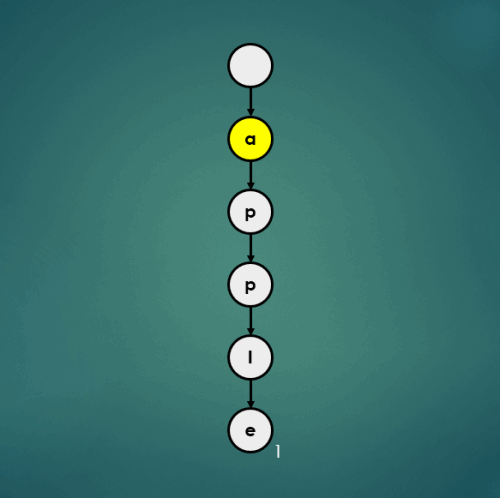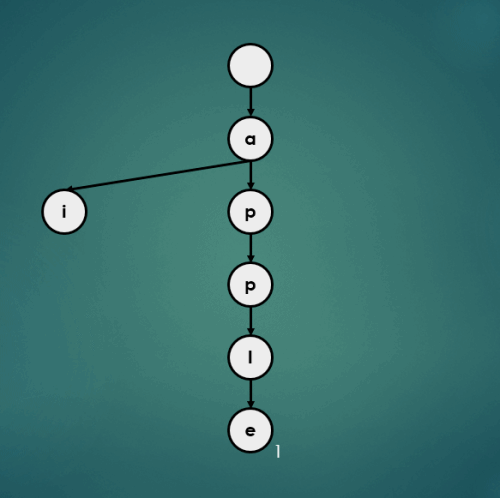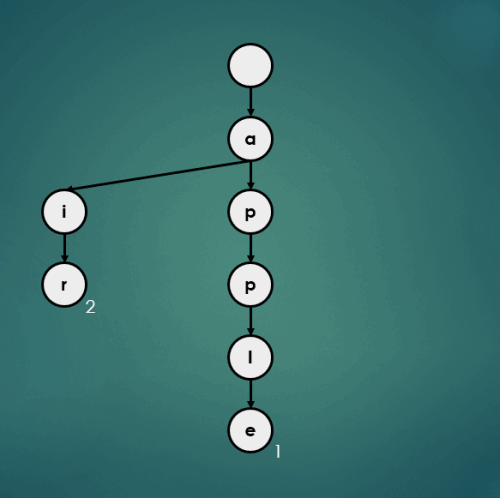
put("air", 2);
3.4.3 “approve”을 키로 가진 데이터 3 삽입
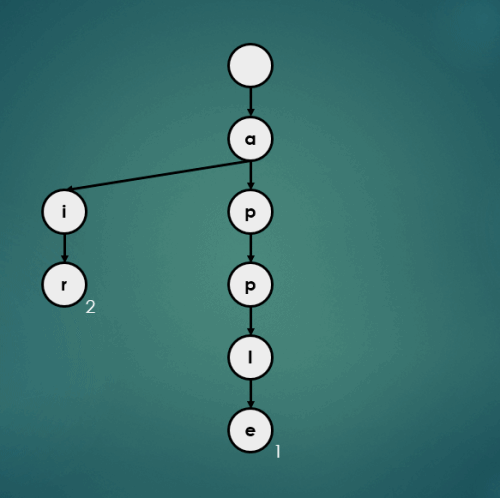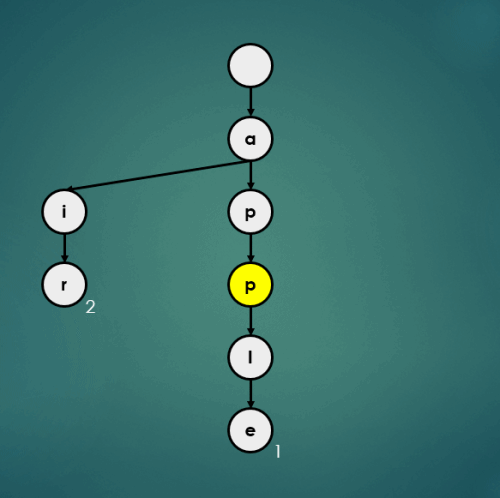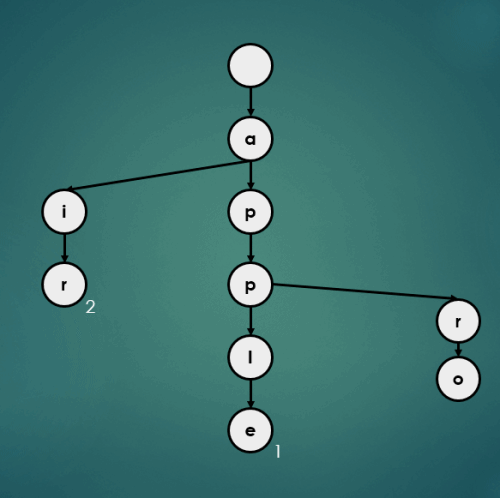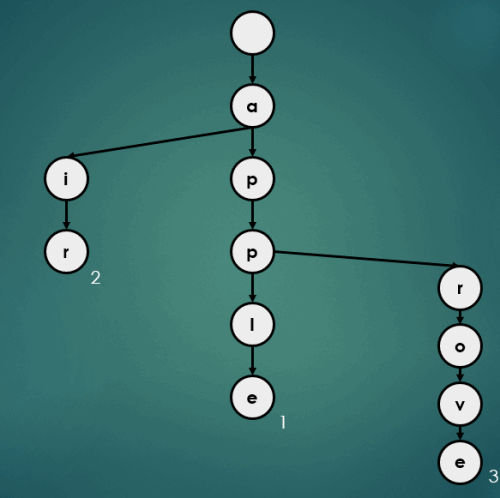
put("approve", 3);
3.4.4 “appa”을 키로 가진 데이터 4 삽입
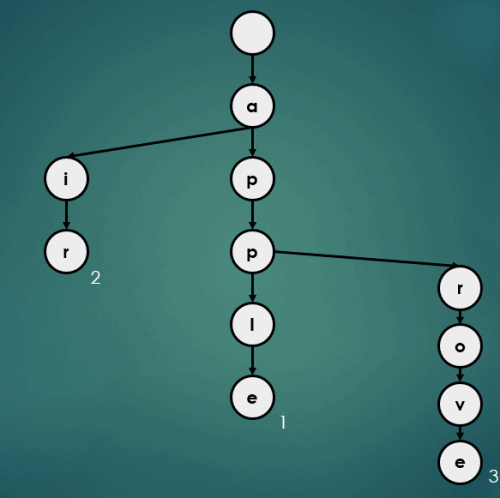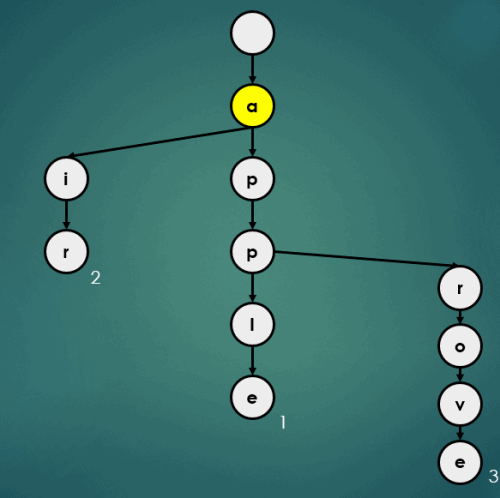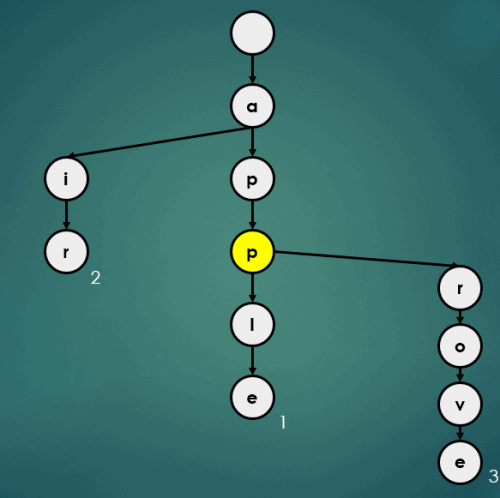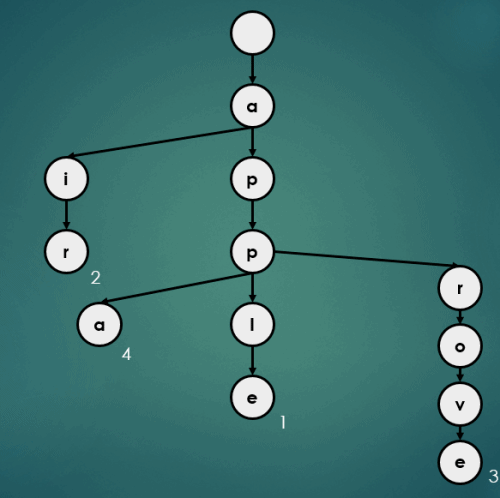
put("appa", 4);
3.4.5 “appb”을 키로 가진 데이터 5 삽입
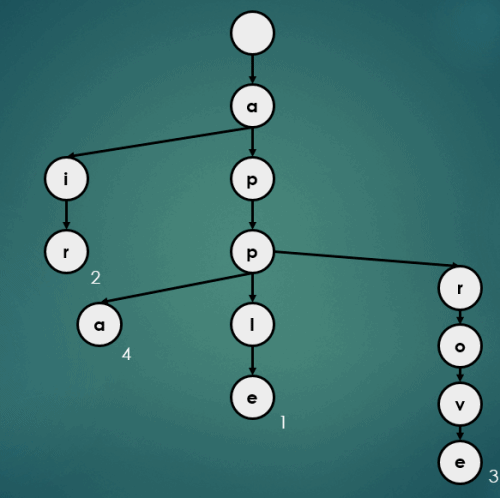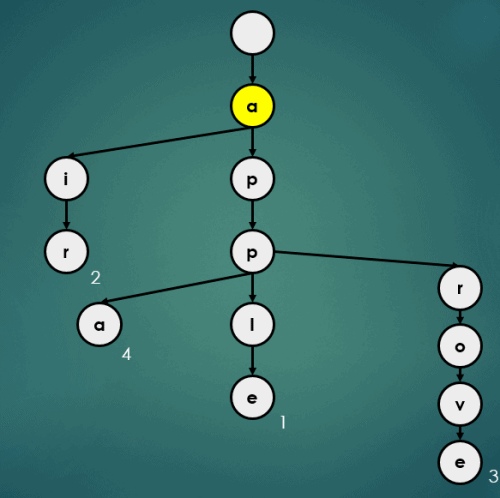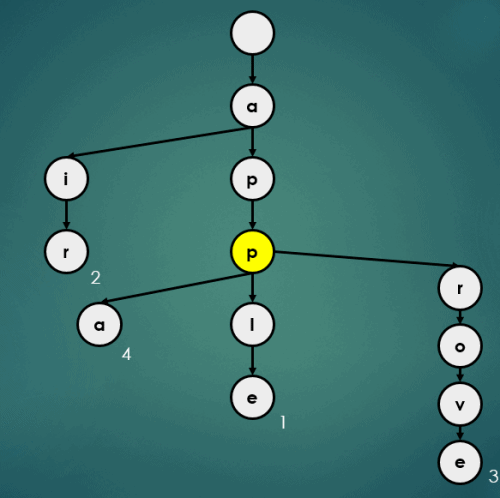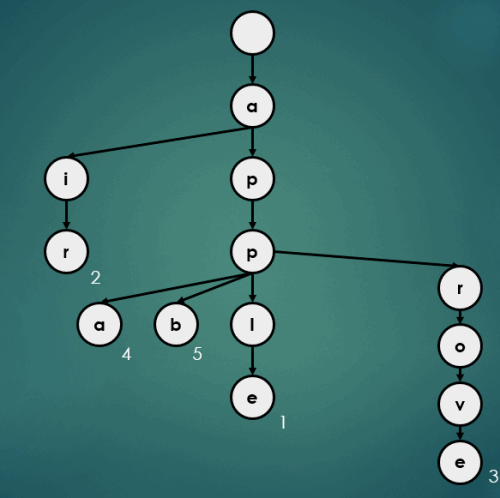
put("appb", 5);
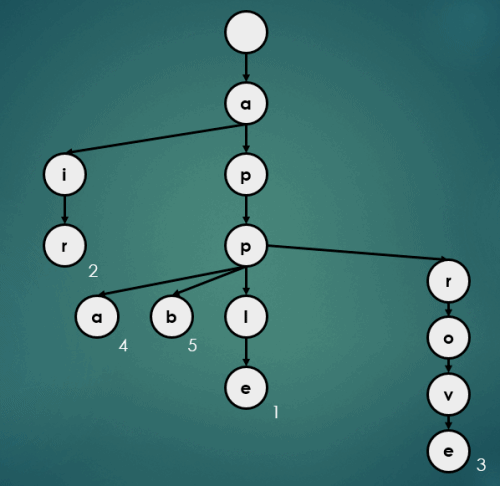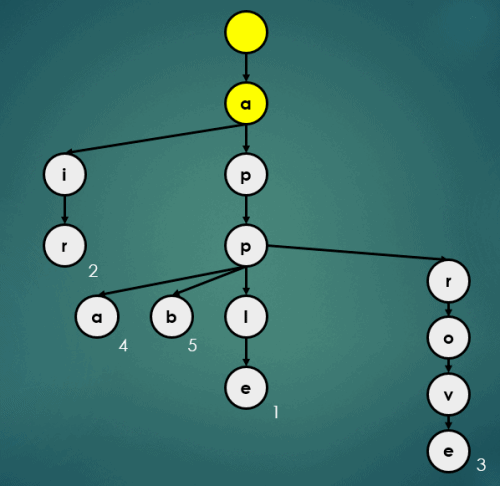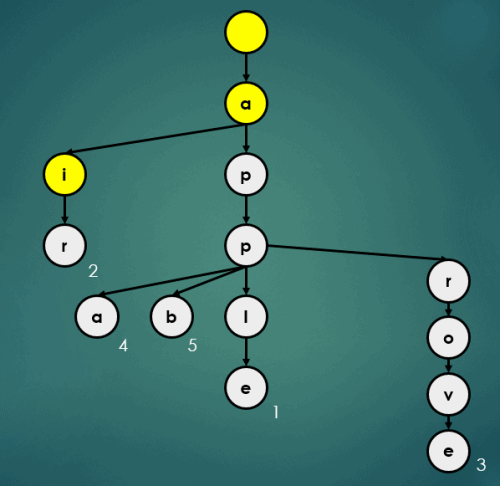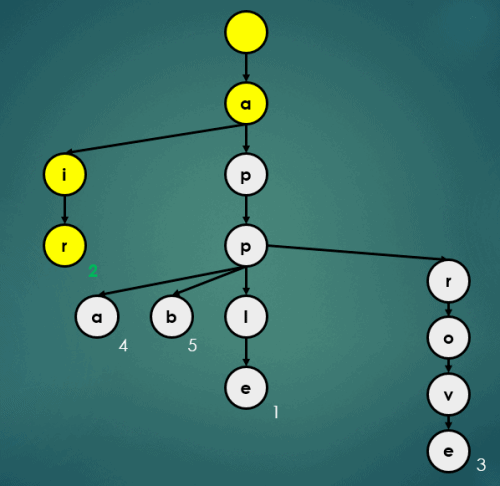
3.5 Map처럼 반환
Trie에서 Map처럼 데이터를 반환하는 과정은 다음과 같다.
3.5.1 “apple”을 키로 가진 데이터 1 반환

get("apple");
3.5.2 “air”을 키로 가진 데이터 2 반환
get("air");
4. Trie 구현
4.1 클래스 작성
Trie를 구현하기 위해 클래스를 아래와 같이 작성한다.
// 노드 클래스
public class Node {
private String character; // 알파벳 문자, 키 값
private int value; // 데이터
private Node[] children; // 하위 노드 배열 변수
private boolean leaf; // leaf 노드 여부 확인
// 생성자
public Node(String character) {
this.character = character; // 알파벳
this.children = new Node[Constants.ALPHABET_SIZE];
}
// getter, setter, toString
public Node getChild(int index) {
return children[index];
}
public void setChild(int index, Node node, int value) {
node.setValue(value);
this.children[index] = node;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public String getCharacter() {
return character;
}
public void setCharacter(String character) {
this.character = character;
}
public Node[] getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(Node[] children) {
this.children = children;
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return leaf;
}
public void setLeaf(boolean leaf) {
this.leaf = leaf;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.character;
}
}
// 상수 클래스
public class Constants {
// 알파벳 문자 수만큼 상수 선언
public static final int ALPHABET_SIZE = 26;
}
// Trie 클래스
public class Trie {
private Node root; // 루트 노드
private int indexOfSingleChild; // 단일 노드의 인덱스
// 생성자
public Trie() {
this.root = new Node(""); // 루트 노드 빈문자열로 초기화
}
// 삽입 메서드
// 탐색 메서드1 : 해당 키가 존재하는지 여부 반환
// 탐색 메서드2 : 해당 키값에 해당하는 값 반환
// 자동완성 메서드
// 가장 긴 접두사 반환 메서드
// 정렬 메서드
}
4.2 삽입
// 삽입 메서드
public void insert(String key, int value) {
Node tempNode = root; // 루트 노드로 초기화
// 입력한 key의 길이 만큼 반복
for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) {
char c = key.charAt(i); // 알파벳 추출
int asciiIndex = transformASCIIIndex(c); // 추출한 알파벳을 배열 인덱스에 맞게 저장할 수 있도록 ascii 값 변환
// 추출한 알파벳을 가진 하위노드가 존재 하지 않으면
if (tempNode.getChild(asciiIndex) == null) {
Node node = new Node(String.valueOf(c)); // 새로운 노드 생성
tempNode.setChild(asciiIndex, node, value); // 하위노드로 세팅
tempNode = node; // 하위 노드로 이동
} else {
tempNode = tempNode.getChild(asciiIndex); // 하위 노드로 이동
}
}
tempNode.setLeaf(true); // 알파벳 문자들의 삽입이 완료되고 마지막 노드를 leaf 노드로 설정
}
// ASCII 값을 배열에 인덱스에 맞게 변환
private int transformASCIIIndex(char c) {
return c - 'a';
}
4.3 탐색
// 탐색 : 해당 키가 존재하는지 여부 반환
public boolean search(String key) {
Node trieNode = root; // 루트 노드로 초기화
// 입력한 key의 길이만큼 반복
for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) {
int asciiIndex = transformASCIIIndex(key.charAt(i)); // 추출한 알파벳을 배열 인덱스에 맞게 ascii 값 변환
if (trieNode.getChild(asciiIndex) == null) { // 추출한 알파벳을 가진 하위 노드가 존재하지 않으면 false 리턴
return false;
} else {
trieNode = trieNode.getChild(asciiIndex); // 하위 노드로 이동
}
}
return true;
}
// 탐색 : 해당 키값에 해당하는 값 반환
public Integer searchAsMap(String key) {
Node trieNode = root; // 루트 노드로 초기화
// 입력한 key의 길이만큼 반복
for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) {
int asciiIndex = transformASCIIIndex(key.charAt(i)); // 추출한 알파벳을 배열 인덱스에 맞게 ascii 값 변환
if (trieNode.getChild(asciiIndex) != null) { // 추출한 알파벳을 가진 하위 노드가 존재하면
trieNode = trieNode.getChild(asciiIndex); // 하위 노드로 이동
} else { // 존재하지 않으면 null 반환
return null;
}
}
return trieNode.getValue();
}
// ASCII 값을 배열에 인덱스에 맞게 변환
private int transformASCIIIndex(char c) {
return c - 'a';
}
4.4 자동완성, 정렬
// Autocomplete : 자동완성
public List<String> allWordsWithPrefix(String prefix) {
Node trieNode = root; // 루트 노드로 초기화
List<String> allWords = new ArrayList<>();
// 접두사 길이 만큼 반복 수행
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
int asciiIndex = transformASCIIIndex(prefix.charAt(i)); // 추출한 알파벳을 배열 인덱스에 맞게 ascii 값 변환
trieNode = trieNode.getChild(asciiIndex); // 하위 노드로 이동
}
collect(trieNode, prefix, allWords); // 접두사 이후의 단어들 모음
return allWords;
}
// 자동완성 단어 수집
private void collect(Node node, String prefix, List<String> allWords) {
// 노드가 null 이면 메서드 종료
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// leaf 노드이면 allWords에 저장
if (node.isLeaf()) {
allWords.add(prefix);
}
// 노드의 자식노드의 수 만큼 반복 수행
for (Node childNode : node.getChildren()) {
if (childNode == null) {
continue;
}
// 자식노드의 알파벳
String childCharacter = childNode.getCharacter();
collect(childNode, prefix + childCharacter, allWords); // 접두사 + 추출한 알파벳, 반복수행을 위해 재귀호출
}
}
// 정렬
public void sort() {
List<String> list = allWordsWithPrefix("");
for (String s : list) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
4.5 가장 긴 접두사 반환
// 가장 긴 접두사 반환
public String longestCommonPrefix() {
Node trieNode = root; // 루트 노드로 초기화
String longestCommonPrefix = ""; // 빈 문자열로 초기화
// 하위노드가 여러개 이거나 leaf 노드일 때까지 반복 수행
while (countNumOfChildren(trieNode) == 1 && !trieNode.isLeaf()) {
trieNode = trieNode.getChild(indexOfSingleChild);
longestCommonPrefix = longestCommonPrefix + String.valueOf((char) (indexOfSingleChild + 'a'));
}
return longestCommonPrefix;
}
// 하위 노드의 갯수 반환
private int countNumOfChildren(Node trieNode) {
int numOfChildren = 0; // 하위 노드 개수 0으로 초기화
// 하위 노드의 개수 만큼 반복 수행
for (int i = 0; i < trieNode.getChildren().length; i++) {
// 하위 노드가 존재하면
if (trieNode.getChild(i) != null) {
numOfChildren++; // 하위 노드 1 증가
indexOfSingleChild = i; // 단일 노드의 인덱스
}
}
return numOfChildren;
}
4.6 코드 테스트
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple", 1);
trie.insert("approve", 2);
trie.insert("air", 3);
trie.insert("appa", 4);
trie.insert("appb", 5);
System.out.println("---- search : true or false ----");
System.out.println(trie.search("apple"));
System.out.println(trie.search("archive"));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---- search : as map ----");
System.out.println(trie.searchAsMap("apple"));
System.out.println(trie.searchAsMap("archive"));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---- autocomplete ----");
System.out.println("a : " + trie.allWordsWithPrefix("a"));
System.out.println("ai : " + trie.allWordsWithPrefix("ai"));
trie.insert("doubles", 6);
trie.insert("yoon", 7);
trie.insert("kim", 8);
trie.insert("park", 9);
trie.insert("lee", 10);
trie.insert("choi", 11);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---- sort ----");
trie.sort();
System.out.println();
Trie trieForCommonPrefix = new Trie();
trieForCommonPrefix.insert("hope", 1);
trieForCommonPrefix.insert("hobby", 2);
trieForCommonPrefix.insert("horror", 3);
trieForCommonPrefix.insert("honor", 4);
trieForCommonPrefix.insert("hospital", 5);
trieForCommonPrefix.insert("horse", 6);
System.out.println("longest common prefix : " + trieForCommonPrefix.longestCommonPrefix());
}
}
---- search : true or false ----
true
false
---- search : as map ----
1
null
---- autocomplete ----
a : [air, appa, appb, apple, approve]
ai : [air]
---- sort ----
air appa appb apple approve choi doubles kim lee park yoon
longest common prefix : ho
5. Reference
본 글은 Udemy의 자바 자료구조 강의를 듣고 개인적으로 학습한 내용 복습하기 위해 작성된 글로 내용상 오류가 있을 수 있습니다. 오류가 있다면 지적 부탁 드리겠습니다.